The first time I realized electrified regionals were truly within reach wasn’t at an airshow—it was on a January site walk at a small Midwestern airport. We were standing beside an old ground power unit while the utility engineer traced his finger across a one-line diagram: “If you want a 2-MW stand here and another at the crosswind pad, we’ll need a new feeder and probably a pad-mount upgrade.” Meanwhile, the Part 23 program manager on our call was asking the FAA analyst about DO-311A abuse testing and how to show fault ride-through on a bussed pack. That’s the shape of the next five years: certification and charging, test reports and transformers. Here’s the candid brief I give operators, airports, and investors when they ask, “Is the FAA ready—and are we?”
Why this matters now (and why regionals go first)
If you fly 9–19 seats on 100–300 nm missions, you’re sitting in the sweet spot for early electrification. Batteries and megawatt-class drives finally close on those stage lengths; the bottlenecks are cert artifacts, ops policy, and whether your airport can pull the amps. From my experience, teams that map routes, reserves, alternates, and grid capacity before they pick an airframe move twice as fast once the conformity builds start.
Certification: the real Part 23 path for electric commuters
Most near-term electric regionals will go through Part 23 (normal/commuter) using performance-based rules and accepted Means of Compliance. In practice, that means:
- Batteries & containment. The FAA recognizes RTCA DO-311A for rechargeable lithium battery performance, abuse, venting, and containment, and ties it to the rechargeable battery TSO. Your design will need pack-level isolation, BMS redundancy, and clear vent paths that don’t feed fumes to the cabin or inlets.
- Propulsion system discipline. Motors, inverters, and controllers are treated with “engine-class” seriousness. Expect early issue papers on motor-inverter integration, thermal management, and single-point failures (plus latent fault detection).
- Systems safety. You still live and die by 23.1309/23.2510-style assessments: functional hazard analysis, DAL allocations for the electric propulsion control system, and a credible story for degraded modes that still make climb limits on a hot day.
From my experience, the fastest programs close software and thermal questions early. If your FADEC-equivalent can show how it derates cleanly across sensor disagreements and your cooling model survives hot-soak turnarounds, the rest of certification reads like a checklist instead of a novel.
If you want the FAA’s broader posture shift in black and white, the MOSAIC final rule is worth a read: it expands Light-Sport and modernizes special airworthiness—with a clear signal that alternative propulsion and performance-based approvals are the direction of travel. It’s not the primary path for 9–19-seat commuters, but it tells you where the Agency’s head is. See: FAA—MOSAIC Final Rule.
What will get scrutinized (so you can be ready)
Here’s what I’ve seen dominate issue papers, conformity reviews, and boardroom updates:
Maintenance & CAW. Battery health trending (SoH/SoC calibration), module swap intervals, and safe de-energization/LOTO procedures tied to training.
Thermal runaway prevention/containment. Abuse testing to DO-311A; proven vent routing; pack isolation logic that’s robust to nuisance trips.
Electrical power quality & protection. DC-bus stability, arcing mitigation, fault ride-through, and protection coordination across packs, contactors, and inverters.
Propulsion control authority. How you allocate torque, how you derate under heat or faults, and how the airplane meets climb/descent safety margins in degraded modes.
Energy reserves & dispatch. Cold-soak derates, alternates, and minimum SoC policies that are conservative and operationally workable.

Airports: are we ready for megawatt charging?
Certification is half the battle; the apron is the other half. Federally obligated airports will need to fold charging into the Airport Layout Plan and coordinate early on siting, safety areas, grounding/bonding, and markings. The FAA’s vertiport/charging engineering materials, while written with AAM in mind, are the best single reference for geometry, lighting, and electrical safety I’ve handed to airport sponsors this year: FAA—Vertiport Design & Engineering Resources.
On capacity planning, don’t guess. Pull 12-month interval load data from your utility, model peak demand charges, and decide whether you’ll need on-site storage or a microgrid. The National Renewable Energy Lab’s aviation work is the cleanest primer I’ve seen on how electrified aircraft interact with airport power systems (resilience, renewables, and demand shaping): NREL—Aviation Electrification.
From my experience, the first airport that instruments everything—bus stability, harmonics, thermal hot spots, turnaround time—writes the playbook the rest of the region copies.
Charging standards: what the FAA expects (and what you should demand)
The FAA doesn’t pick a connector, but it does expect interoperability and a safety case that covers clearances, grounding, markings, and emergency procedures. Airports should declare the chosen interface in ALP/7460 filings and show compliance with applicable electrical and airside standards. Operators should push vendors toward open, aviation-grade standards with field-upgradable firmware. That posture not only fits the FAA’s performance-based approach—it also keeps you eligible for funding streams that require broadly accessible infrastructure.
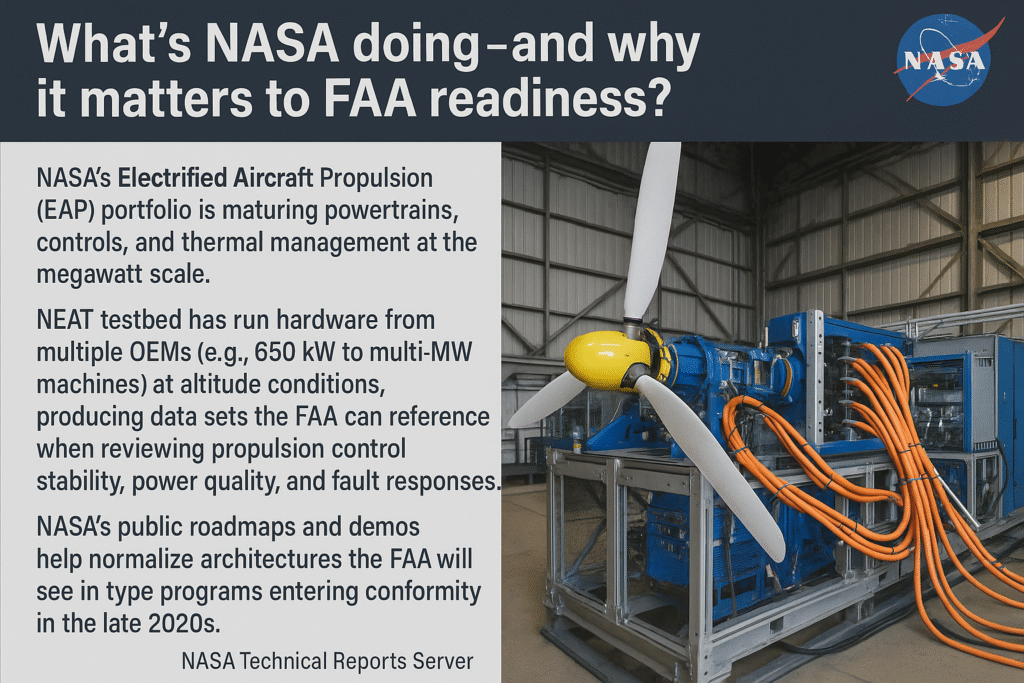
NASA’s role (and why it helps you in certification)
NASA’s Electrified Aircraft Propulsion portfolio is quietly doing a lot of heavy lifting for everyone—maturing megawatt-class powertrains, controls, and thermal management at altitude conditions. The NEAT testbed has exercised 650 kW to multi-MW machines and published power-quality and fault-response data sets that FAA engineers recognize when they review your protection and stability story. If you need a single external explainer for executives or city councils, this is it: NASA—Electrified Aircraft Propulsion.
A fictional—but realistic—mini case: closing the gaps before conformity
Operator: 12-aircraft electric commuter startup, 9 seats, two bases, 140–180 nm routes.
Airport/utility reality: Existing substation at 80% summer peak; feeder re-conductor required for a second 1.5 MW stand.
Certification reality: DAL B assigned to the propulsion control computer; pack-level isolation validated for single-fault but not yet for latent fault + sensor drift; cold-soak reserves modeled with mild pessimism.
What we changed:
- Pulled actual interval data and staged a 1.5 MW stand at Base A with a 500-kWh buffer battery to shave peaks; delayed Base B’s second stand to Phase 2.
- Rewrote the FADEC-equivalent derate logic to add a timed torque-sharing mode under sensor disagreement; validated on the iron bird before flight.
- Hardened the reserve policy: EOL batteries at 20% degradation and −10 °C cold-soak must still yield alternate + 30 minutes with a realistic headwind.
Outcome: The ACO closed two issue papers; the ADO approved an ALP update with conditions; the utility issued a construction schedule; and the board finally saw a runway that wasn’t made of hope.
Ops, training, and MEL philosophy (the human layer)
Expect type- or model-specific differences training that focuses on energy management: pre-dispatch SoC checks, cold-soak derates, and what “one pack isolated” means for performance. Ops specs will codify minimum departure SoC, turn-time for charging, and alternate strategy. Your MEL needs to talk in the language of packs, contactors, and thermal controllers—what’s dispatchable, for how long, and with which performance penalties.
A mistake I see a lot: treating energy readouts like fuel gauges. They aren’t. Design your HMI for unambiguous SoC, range rings, and reserve buffers, and keep abnormal checklists short and decisive.Server
Risk checklist I hand to program managers
- Supply chain. UL/IEC/RTCA evidence for cells/modules; second sources for contactors, sensors, and HV cabling; AS9100 flow-downs in supplier traveler packets.
- Thermal engineering. Cooling sized for climb-power holds and hot-day turnarounds; automated derates with crisp cockpit cues.
- Interoperability. Chargers with open comms and field-upgradable firmware; spare parts and trained techs on-airport.
- Documentation. AFM/POH, AMM, and MEL aligned with battery maintenance and dispatch policies; conformity artifacts audit-ready.
Where you’ll see near-term movement
Watch for FAA special conditions and issue papers on electric propulsion units; NASA/industry megawatt tests feeding consensus standards; and airports publishing ALP updates that include charging. Those three threads tell you how fast regional electric fleets can move from trials to schedules.
Bottom line: Is the FAA “ready” for electric regionals?
Ready in the way that matters. The FAA is using performance-based Part 23, recognized battery standards, and targeted issue papers to clear the first electric regionals—while MOSAIC modernizes adjacent categories and signals flexibility going forward. Airports are being told to plan charging into ALPs and coordinate early with utilities. NASA is generating MW-scale propulsion data the FAA can lean on. It’s not turnkey, but it’s actionable—if operators, airports, and OEMs engage early and share data.
If you’re building your own roadmap, pair propulsion gains with airframe efficiency to stretch range and margin. Our deep dive on Sustainable Engine Technologies shows how cleaner combustors and hot-section materials complement hybrid-electric assists. For airframe wins that turn watts into miles, see Morphing Wing Technology 2025: Biomimicry & Efficiency. And keep an eye on policy shifts that nudge reserve rules, MEL philosophy, or airport funding—we summarize the “so what” for operators in Regulatory Updates.






