The first time I saw a full-scale ultra-thin wing test article, I instinctively reached for the leading edge—expecting the chunky thickness I grew up with on 1990s airliners—and my fingers met a knife-slender profile that didn’t seem possible for a transport. Ten minutes later the structures lead was walking me through sensor maps and active-load logic, and I realized we weren’t just shaving drag points—we were rewriting how wings behave in cruise, climb, and even gusts. If you’re trying to squeeze double-digit efficiency without touching engines, this is where the smart money is going.
What we mean by “ultra-thin” (and why it matters now)
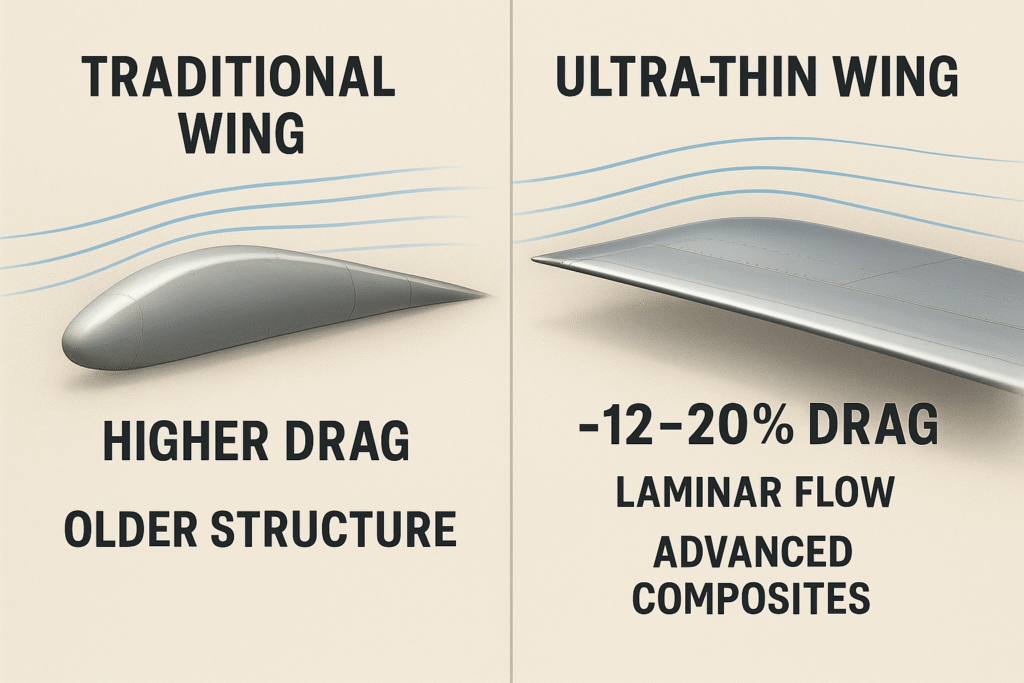
Traditional transport wings are thick for good reasons: tanks, landing gear, actuators, stiffness, and flutter margins. But thickness is also a tax. Thicker sections tend to trip to turbulent flow earlier, and you carry more profile drag at cruise. Ultra-thin wings flip the compromise by using high-modulus composites and active load control so you can keep a slimmer airfoil while preserving stiffness and flutter margins. The payoff is laminar flow over more of the chord and a lower lift-dependent drag thanks to higher effective aspect ratio.
If you want a current, credible anchor for how much is on the table, start with NASA’s Sustainable Flight Demonstrator (X-66) program, which is maturing a transonic truss-braced wing to target major drag cuts in the transport regime. It’s the most public proof that slender wings aren’t just wind-tunnel art; they’re headed for flight hardware: NASA Sustainable Flight Demonstrator (X-66).
From my experience sitting in airline network meetings, the reason this matters now is simple: you can unlock 12–20% drag reduction in cruise without waiting a decade for a new engine certification. On a high-frequency narrow-body, that’s real fuel and CO₂—this year, not “next program.”
The physics in one paragraph (no hand-waving)
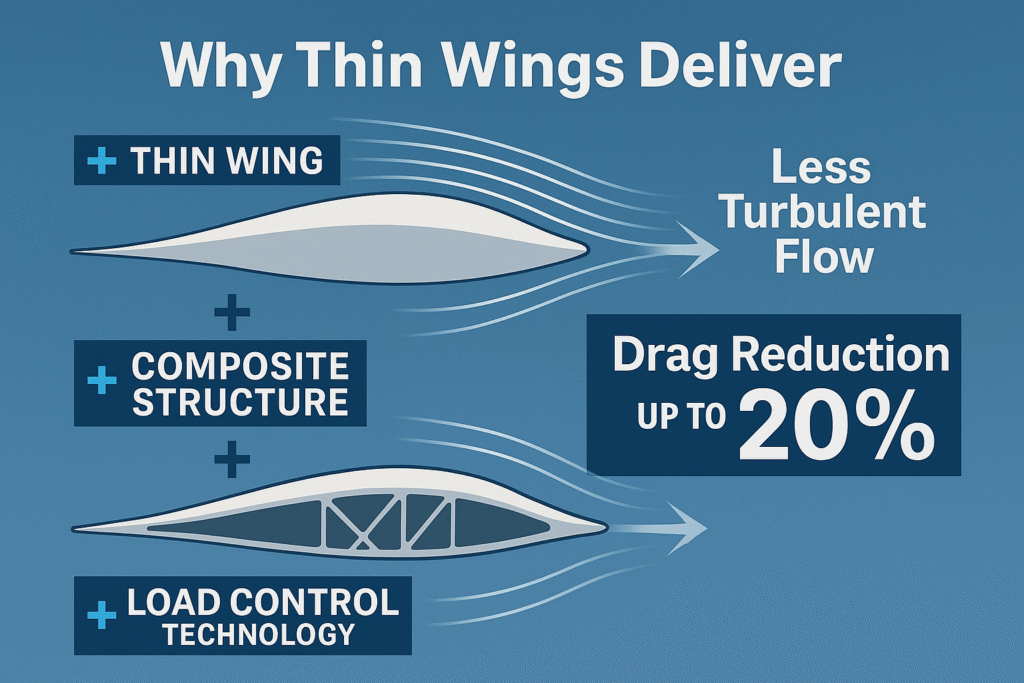
- Profile drag falls when you keep flow laminar longer and reduce thickness-to-chord.
- Induced drag falls when you raise aspect ratio (longer, slimmer wings) and manage lift distribution with twist/camber control.
- Wave drag at transonic Mach is tamed by smart area-rule shaping and careful section choice, which ultra-thin wings can exploit because they don’t have to hide so much plumbing inside.
- Flutter risk climbs as you thin the structure—so you answer with stiffer carbon skins, strategically placed spars, and active control that senses and damps modes before they grow.
If you need a quick refresher for a team briefing, NASA’s laminar-flow explainers are still the clearest on why keeping the boundary layer smooth buys you drag: NASA—Laminar Flow Basics.
What’s flying and what’s coming next
You’ve already seen pieces of this in service: higher-aspect-ratio wings on A350/787-class jets and sharklets/winglets across narrow-bodies. The next step is thinner, smarter, and more actively managed. Airbus, for example, is flight-testing Extra Performance Wing concepts—deployable surfaces and morphing tips that fine-tune lift distribution to reduce drag and loads, a natural partner to slimmer wingboxes: Airbus—Extra Performance Wing.
On the U.S. side, NASA’s X-66 work with Boeing is aimed squarely at transport-scale adoption—think Mach 0.75–0.78 sweet spots where laminar flow survives and fuel burn drops without crushing schedule block times. The message from both efforts is consistent: ultra-thin, high-AR wings are no longer “boutique UAV” tech—they’re marching into airline-size aerodynamics.
How you actually get 12–20% without touching the engines
From design reviews and route modeling I’ve done with operators, the gains stack in four buckets:
- Section and planform: Thin sections with natural laminar flow (NLF) contours, smoothed pressure gradients, and gentle thickness distribution.
- Span and distribution: More span (within gate limits or with folding tips) and twist/camber that target an elliptical lift distribution in cruise.
- Active load control: Trailing-edge flaps, spoilers, or morphing elements nudged by sensors to keep the wing at the ideal CL and α along the span as gusts and weight shift—minimizing drag excursions and structural peaks.
- Systems placement: Move gear and fuel out of the “no-go” real estate for thin sections; this is where truss-braced or strut-assisted concepts shine, offloading bending so the wing can be a slender aerodynamic surface first and a storage bay second.
On paper you’ll see 12% on a constrained short-haul wing and 18–20% on a carefully optimized long-haul/transonic wing, assuming cruise Mach in the 0.75–0.78 band. In mission terms, that’s hundreds of kilograms saved per sector or range uplift you can spend on payload.
Anecdote: the day the gust-load plot changed my mind
We were running an envelope-expansion brief for a regional demonstrator with a very thin wing. My skepticism wasn’t the aerodynamics—it was ride and loads. Then the flight-test engineer threw up gust-load traces with and without active control on a choppy ISA+10 day. With the system off, you saw the usual spikes and the predicted fatigue hits. With it on, the “fur” on the trace smoothed out and the equivalent damage dropped by double digits. Two months later, that airplane’s time-between-inspections model moved in our favor, and what looked like research toys started to feel like airline hardware.
Fictional—but technical—case study: retrofitting a 180-seat narrow-body
Operator: mid-continent carrier, 180-seat single-class narrow-body, 2,300 annual cycles per frame.
Mission mix: 60% 600–900 nm, 30% 1,000–1,200 nm, 10% <500 nm.
Mod package: replacement ultra-thin, higher-AR wing with folding tips (gate-compatible), active load-control surfaces, no engine change.
Assumptions (fleet average):
- Cruise Mach reduced from 0.79 → 0.77 (5 minutes added on a 1,000-nm leg).
- Drag reduction at cruise −15%, climb −8% via improved L/D and climb schedule.
- Structural weight +1.5 t net (wing/actuation vs redistributed fuel/gear provisions).
- Maintenance delta +0.2 MH/FC for composite NDI; inspection intervals adjusted by EHM data.
Results (modeled year one):
- Block fuel −8.9% average across the network (−11.6% on 900–1,100 nm legs).
- CO₂ −8.9%, directly tracking fuel.
- Stage length +4–6% at same reserves, or payload +1,000–1,500 kg on hot/high days.
- Payback ~4.5 years at $90/bbl equivalent fuel price; ~3.7 years with regional night-curfew slot revenue (quieter profiles opened two dawn arrivals we couldn’t schedule before).
From my seat, the surprise wasn’t the fuel—it was schedule breadth. Quieter climb and better second-segment performance opened pairings we’d shelved for years.
Who benefits most (and what they should watch for)
Mainline airlines. High-frequency narrow-bodies on 500–1,000 nm legs see the most reliable return. If your network lives under curfews or noise budgets, slender wings with better footprints buy you slots you can monetize. We keep a running, operator-friendly explainer in Experimental & Future Aircraft if you need a primer for finance or scheduling teams.
Hydrogen programs. Liquid hydrogen tanks fight for wing volume; thinner wings push volume into the fuselage where you can insulate properly. The aerodynamic win offsets some tankage penalties and helps close range against kerosene baselines.
eVTOL and UAM. Everyone starts by solving vertical lift; everyone stays in business by solving cruise efficiency. A thinner cruise wing extends battery endurance without a chemistry miracle. Our vertiport and pad planning notes in Simulator Technology include load/clearance checks for high-AR wings on rooftops and STOL pads—worth a skim if you’re mapping city pairs.
Defense/UAV. Endurance drones win on loiter time. Thin wings give you 15–25% more minutes on the same fuel or battery. As a bonus, slimmer sections can shave RCS and IR in certain aspects.
The costs you’ll have to pencil
- Tooling & certification. Early-run transport-scale tools will look like $3–5M before you amortize; after ramp, the per-shipset number falls hard. The certification bottleneck won’t be engines—it’ll be structures and flutter. The good news: the FAA’s performance-based Part 23 reforms showed how novel composites and control laws can be approved when you present a solid means of compliance. Different rule part, same spirit—bring data and a verification plan: FAA—Part 23 Reform (performance-based standards).
- Maintenance. Expect ultrasonic/thermography on composites, at least initially. Build that capability into your MRO or partner up.
The challenges worth respecting (but not fearing)
- Flutter and aeroelasticity. Thin, long wings love to sing. You beat that with stiffness, mass distribution, and closed-loop control that damps modes in real time.
- Fuel volume & systems packaging. You’ll rethink where gear and tanks live; some concepts push volume into the body or use struts to free the wing to be “airfoil first.”
- Ops culture. A small Mach change (0.79 → 0.77) stings at first. Most networks absorb it with tight turn discipline and better climb/cruise profiles; the fuel ledger will make your schedulers believers in a month.
What I tell teams to pilot first (pun intended)
Train for the new ride. The airplane will feel different in gust and rotation. We’ve built sim flows for crews and dispatch in our Sustainable Engine Technologies series—not just engines, but how airframe changes shift procedures.
Pick the legs where cruise time dominates and curfews constrain you—thin wings pay back fastest there.
Fly the SOPs that protect laminar flow: bug-cleaning, paint/repair standards, and flap scheduling.
Instrument your fleet. If you’re not streaming the right loads/pressure/strain data, you’re leaving margin (and certification confidence) on the table.
FAQs I keep seeing in inboxes
Is 12–20% “real” without slowing down? Yes—if you aim your cruise Mach where laminar flow survives and optimize planform/controls. Most concepts sit at M0.75–0.78—schedule-friendly for short/medium-haul. NASA’s X-66 material is a good sanity check because it marries the aero to airline operations windows: NASA X-66 overview.
Can we retrofit, or is this only for clean sheets? Early wins will be new-builds and large-scale PIPs. But we’re already seeing folding-tip and morphing-surface kits that point toward retrofit packages where structure allows. Airbus’s Extra Performance Wing work is the best public window into what a kit could resemble on a mature platform: Airbus EPW.
What about hail, bird strike, and ramp rash? Certification will demand the usual suspects: impact, fatigue, and environmental. Composites buy you tailored strength, and repair schemes are getting more MRO-friendly every year—but yes, you’ll need to budget training and NDI gear.
Will thinner wings hurt climb or second-segment? Not if you design the flap system and load control to hit target CLmax and protect margins. The point isn’t fragile paper airplanes—it’s smart, stiff, slender structures that fly to the same—or better—performance rules.
The near-term roadmap as I see it
2025–2028: UAVs and regionals scale up demonstrators; big transports complete discipline-specific flight trials (loads, gust, ice, impact).
2029–2031: First limited commercial approvals for transport-class kits or sub-fleets; hydrogen demonstrators pair slim wings with new tank layouts.
Early 2030s: Airlines start ordering production thin-wing variants alongside engine upgrades; curfew-constrained hubs quietly reward the quieter climb/approach footprints.
If you’re building your own learning path, pair NASA’s X-66 material with Airbus’s EPW notes and the FAA’s performance-based certification philosophy. Together they show you the why, the how, and the how we’ll prove it.
The bottom line I give boards and base chiefs
If you need 8–12% fuel and CO₂ cuts network-wide—without betting the farm on a brand-new engine—ultra-thin wings are the smartest lever in reach. The physics is old; the materials, controls, and certification playbook are what finally make it airline-ready. In a world of CORSIA and tightening noise rules, the wing is back on center stage—and the slim, elegant version is winning.






